Overview
Heart palpitations refer to an abnormal awareness of the heartbeat, often described as a fluttering, pounding, racing, or irregular sensation in the chest. While palpitations are often harmless, they can sometimes indicate an underlying arrhythmia, which is a disorder of the heart’s electrical activity that causes it to beat too fast, too slow, or irregularly.
Arrhythmias range from mild, benign conditions to severe, life-threatening disorders. Some common terms and types include:
- Tachycardia: A resting heart rate that is too fast (above 100 beats per minute).
- Bradycardia: A resting heart rate that is too slow (below 60 beats per minute).
- Atrial Fibrillation (AFib): An irregular and often rapid heartbeat that increases stroke risk.
- Ventricular Arrhythmias: Abnormal rhythms that originate in the heart’s lower main pumping chambers, potentially leading to cardiac arrest.
Risk Factors
Heart palpitations and arrhythmias can be triggered by various factors, including:
- Stress & Anxiety: Emotional distress or panic attacks can cause palpitations.
- Stimulants: Excessive caffeine, nicotine, alcohol, or certain medications can affect heart rhythm.
- Electrolyte Imbalances: Low potassium, magnesium, or calcium levels can disrupt the heart’s electrical activity.
- Heart Conditions: Coronary artery disease, heart failure, or valve disorders can lead to arrhythmias. These are the main conditions to detect or exclude in cases of arrhythmias.
- Thyroid Disorders: An overactive or underactive thyroid can cause heart rhythm abnormalities.
- Sleep Apnea: Poor oxygen supply during sleep can trigger irregular heartbeats.
- Genetic Factors: Some arrhythmias run in families and may be hereditary.
Symptoms
Symptoms vary depending on the type and severity of arrhythmia but often include:
- Palpitations: A fluttering, pounding, or irregular heartbeat.
- Dizziness or Lightheadedness: Reduced blood flow may cause faintness.
- Shortness of Breath: Difficulty breathing, especially during activity.
- Chest Pain or Discomfort: A sensation of tightness or pressure in the chest.
- Fatigue & Weakness: Poor circulation can lead to tiredness and reduced energy.
- Fainting or Near-Fainting Episodes: A severe arrhythmia may temporarily reduce blood flow to the brain, leading to syncope (fainting).
Diagnosis
Dr. Fady Turquieh may recommend various tests to diagnose arrhythmias, including:
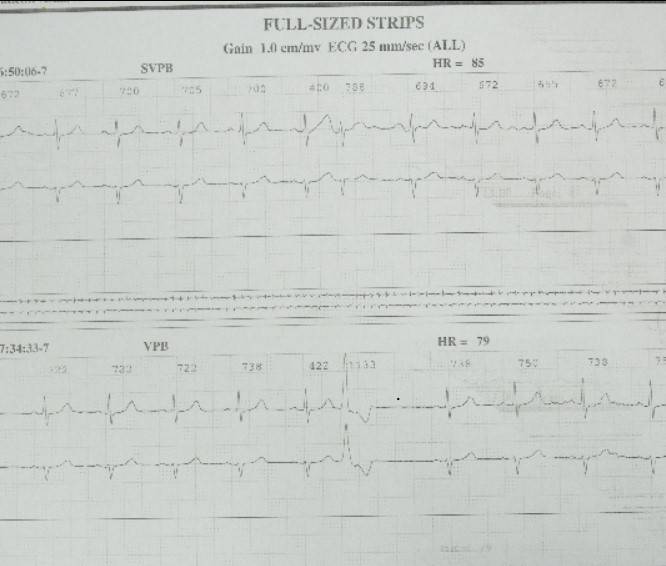
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): A quick test to measure heart rhythm and electrical activity.
- Holter Monitor: A portable ECG worn for a day and up to a week to track irregularities and detect the type of arrhythmia
- Event Recorder: A longer-term monitoring device for detecting intermittent arrhythmias.
- Echocardiogram: Uses ultrasound to assess heart structure and function.
- Stress Test: Evaluates how the heart and particularly the electrical system responds to physical exertion.
- Electrophysiology Study (EPS): A specialized test to map the heart’s electrical pathways.
Treatment
The treatment for heart palpitations and arrhythmias depends on their cause, severity, and impact on overall heart health.
Lifestyle Modifications:
- Reducing Stimulants: Limiting caffeine, alcohol, and nicotine.
- Managing Stress: Techniques like meditation, breathing exercises, and yoga can help regulate heart rate.
- Staying Hydrated & Maintaining Electrolyte Balance: Ensuring proper levels of potassium and magnesium can support heart function.
Medications
- Beta-Blockers & Calcium Channel Blockers: Help slow the heart rate and reduce palpitations.
- Antiarrhythmic Drugs: Used to restore and maintain a normal heart rhythm.
- Anticoagulants (Blood Thinners): Recommended for conditions like atrial fibrillation to prevent stroke.
Medical Procedures & Devices
- Cardioversion: A controlled electrical shock to reset the heart’s rhythm.
- Catheter Ablation: A minimally invasive procedure to destroy abnormal electrical pathways causing arrhythmias.
- Pacemaker Implantation: A small device implanted under the skin to regulate slow heartbeats.
- Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator (ICD): A device that detects and corrects dangerous heart rhythms.
Early diagnosis and treatment of arrhythmias are essential in preventing complications such as stroke, heart failure, and sudden cardiac arrest. Dr. Fady Turquieh specializes in accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plans to ensure optimal heart health for his patients.
